Contents
SEO isn’t only about optimizing your front-facing content. The technical backend processes are just as critical, including improving site speed, optimizing visual elements for mobile screens, and having an XML sitemap and robots.txt file for search engine bots to crawl your website accurately.
Without technical SEO, the frontend SEO aspects won’t generate positive results. We’ve created this guide to help website owners implement the right technical SEO techniques.
SEO basics & setup
Technical SEO starts with tracking your website’s search performance. This tracking covers both search rankings and technical factors like page speed and mobile usability. Let’s explore effective ways to track your website performance.
Set up Google Search Console & Bing Webmaster Tools
Google and Bing, the number one and two search engines worldwide, provide tools to help website owners easily track their search rankings and technical performance. Google has the Search Console, and Bing has Webmaster Tools. You can sign up for these tools for free and connect your website. The only requirement is verifying your domain by following either platform’s on-screen instructions.
Install and configure Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is a free tool for tracking your website traffic. With this tool, you can monitor all website visitors, including their locations, devices, operating systems, and average time spent. You can set it up for free at analytics.google.com. Like with Search Console, the main requirement is verifying your domain name ownership.
Establish KPIs for future success
You need precise KPIs aligned with your SEO goals. These KPIs define what you want to achieve with your technical SEO efforts. Examples are:
- Page speed. Your website should load in 3 seconds or less to boost SEO performance.
- Keyword rankings. Always aim to rank number one for popular keywords in your niche.
- Bounce rate. This metric indicates how quickly people leave your site after viewing only one page. 40% or lower should be your target bounce rate.
- Conversion rate. This indicates the percentage of visitors who perform a suggested action on your website, e.g., signing up or buying a product. 2% to 5% should be your target.
Set up rank tracking tools (local and global)
Sign up for a rank tracking tool to monitor your website’s search rankings both locally and internationally. With this tool, you can monitor your site’s keyword performance in specific regions (e.g., Europe or North America) or countries. Nightwatch, Mangools, and Ranktracker are popular rank tracking platforms.
Use SEO tools like Semrush for audits and competitor analysis
With dedicated SEO tools like Semrush, you can audit your website to discover any optimization-related issues. These tools identify problems like duplicate content, server errors, and crawl errors, and you can quickly fix them. These tools also analyze competitors’ search rankings to help you understand how to outrank them.
Crawling, indexing, and accessibility
Search engines deploy automated bots, known as crawlers, to find and download web pages for their indexes. These crawlers scour through your website and index the pages that will rank on search results. However, they aren’t all-seeing. You’ll need to guide them to index the right pages and ignore the non-essential ones. Comprehensive technical seo checklists always include optimizing your website for efficient indexing, so let’s explore how to do that.
Check site indexing status (GSC coverage report)
We’ve discussed setting up Google Search Console (GSC) earlier. After setting it up, you can access your coverage report by clicking on Pages under the left Indexing menu. The report looks like this:
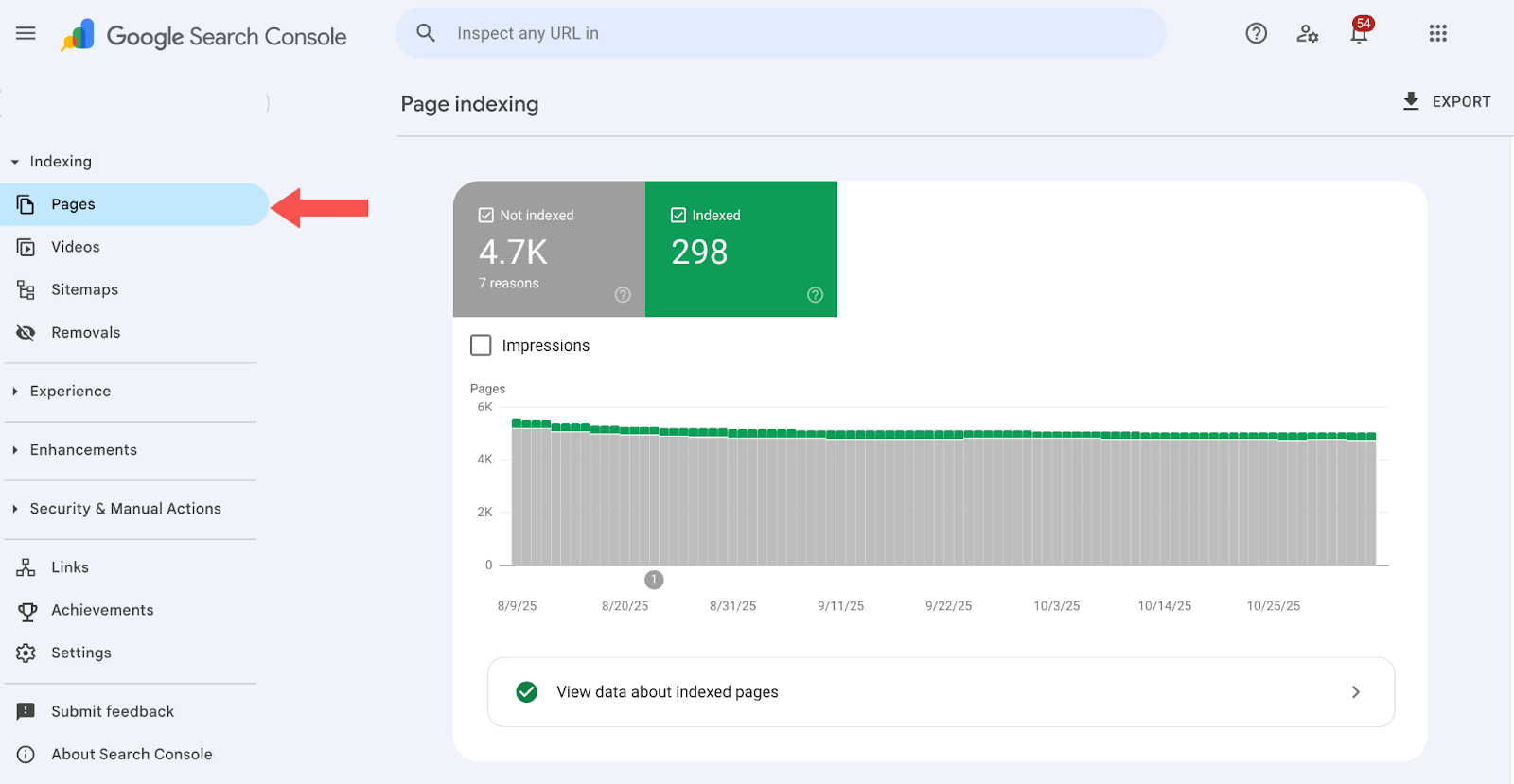
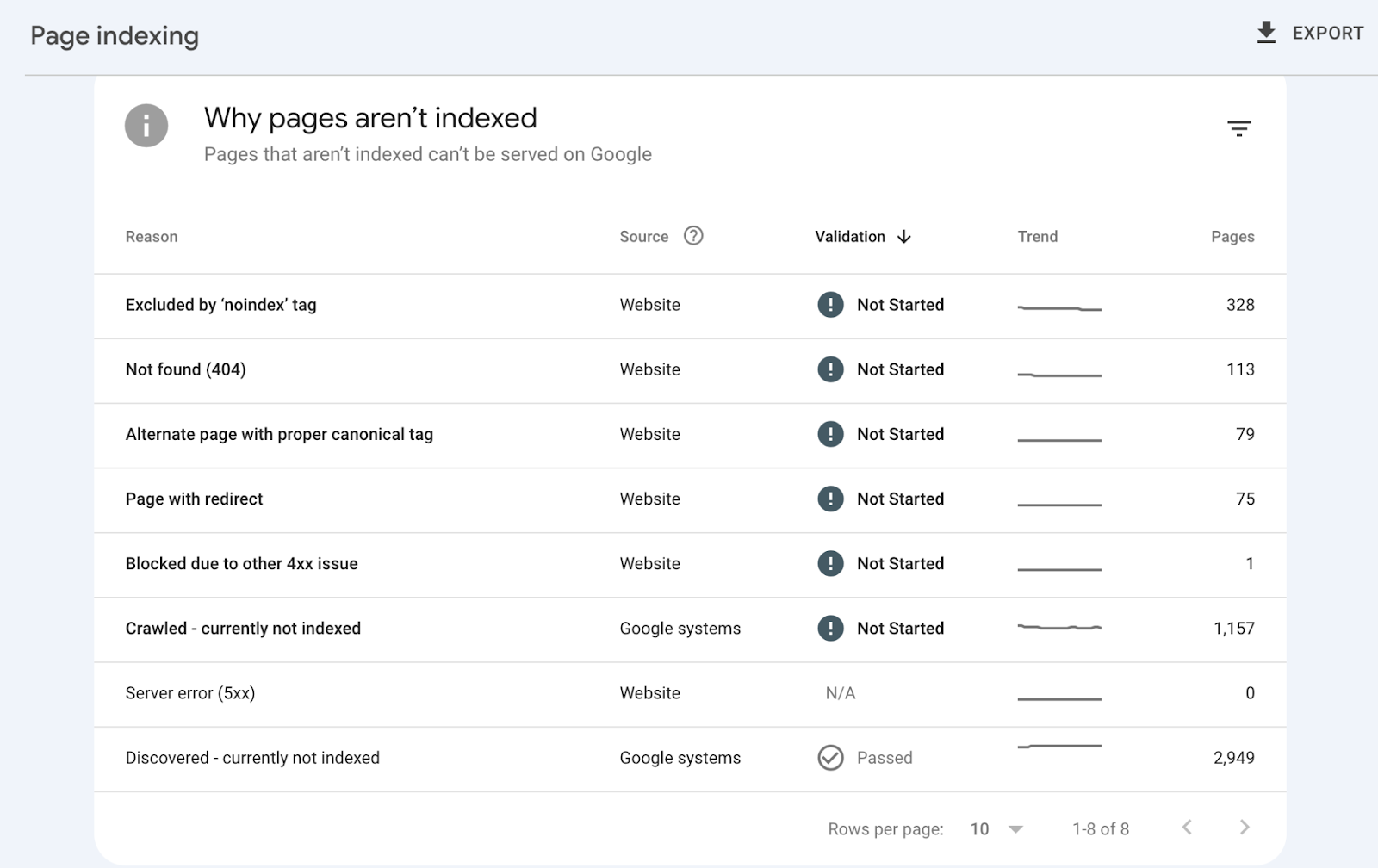
It shows how many of your website’s pages have been indexed and which pages are non-indexed, along with the reasons for non-indexing. If pages are non-indexed because of errors like Not found (404) or redirect chains, you can correct them.
Fix crawl errors and ensure all important pages are crawlable
The GSC coverage report shows pages with crawl errors, like 404 Not Found or crawled but not currently indexed. You can view all these pages and correct them from your website’s backend. After correction, Google’s crawlers can add these pages to their index and suggest them in search results.
Review and optimize the robots.txt file correctly
A robots.txt file instructs search engine crawlers on which pages they’re allowed to crawl and which are restricted. For example, you can instruct crawlers to avoid indexing admin pages, private pages, and test pages with duplicate content. If you don’t include this command in your robots.txt file, crawlers will index anything they encounter and may suggest irrelevant content to users.
You should generate a detailed robots.txt file and upload it to your website’s directory, where crawlers can always find it.
Review this file regularly and make any necessary adjustments. The goal is to ensure that crawlers index only the right pages.
Avoid blocking critical pages or resources
In a robots.txt file, you may mistakenly block crawlers from indexing an essential page, e.g., your blog posts. That’s why we advised frequently reviewing your robots.txt file and making needed changes. This file controls what crawlers index from your website, and any mistake can quickly reduce your website traffic, so always review it for errors.
Resolve redirect chains and loops
A redirect chain is a common error where a page link redirects to multiple pages before landing at a final destination. Crawlers have limited crawl budgets per site, and this redirect chain causes them to spend too much budget following redirects rather than indexing more essential pages.
Resolve any redirect loops identified in the GSC coverage report — you can do this by using 301 permanent redirects. Overall, minimize the number of redirects in the first place, as this reduces the number of potential crawling errors.
Ensure single canonical version (HTTP/HTTPS, www vs non-www)
Websites have www and non-www versions and also HTTP and HTTPS versions. This leads to sites having multiple versions of the same URL, e.g., page.com, www.page.com, http://page.com, and https://www.page.com.
To avoid confusing crawlers, ensure there’s a single canonical version of each web page address, also known as canonicalization.
This means designating one URL as the official source that can be accessed through different URLs. To do this, create a permanent redirect in your domain name settings, ensuring every request gets redirected to the full link: https://www.[YourDomainName].com. This permanent redirection automatically forwards web crawlers to a single canonical version and avoids getting confused by multiple links.
Submit and optimize XML sitemap (clean, up-to-date)
A sitemap is a file that lists all URLs on your website, helping crawlers to crawl and discover all relevant links. It gives crawlers accurate information about your site structure, as if a crawler were entering a building and seeing a detailed map of all the rooms.
The sitemap is written in Extensible Markup Language (XML) format. You don’t have to write the sitemap manually. Rather, use an automated sitemap generator to create one for your website. After creating the sitemap, you can submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools for indexing.
Use meta robots tags properly (noindex/nofollow)
Use proper meta tags to guide crawlers in indexing a specific web page. For example, attaching the nofollow tag to a link tells crawlers not to follow the link, and attaching the noindex tag to a page tells crawlers not to index the page. You can add these tags by editing your site’s HTML code or via your content management system (CMS).
Use hreflang tags for international/multilingual sites
If your site is multilingual, with separate language versions of each page, use hreflang tags to tell crawlers which page to index for different audiences. For example, if you have both English and Italian pages, the English page’s code will include a hreftag pointing to the Italian page, and vice versa. These tags inform crawlers about the respective language versions instead of thinking both pages are duplicate content.
Keep your crawling and indexing under control
Our team takes on the complex parts and keeps your structure easy to maintain.
Site architecture & navigation
Your site’s architecture is a key contributor to its search rankings. Factors like internal linking, mobile-first optimization, and simple navigation are considered by search engine algorithms, so they can’t be ignored. Let’s explore how to optimize your site architecture below.
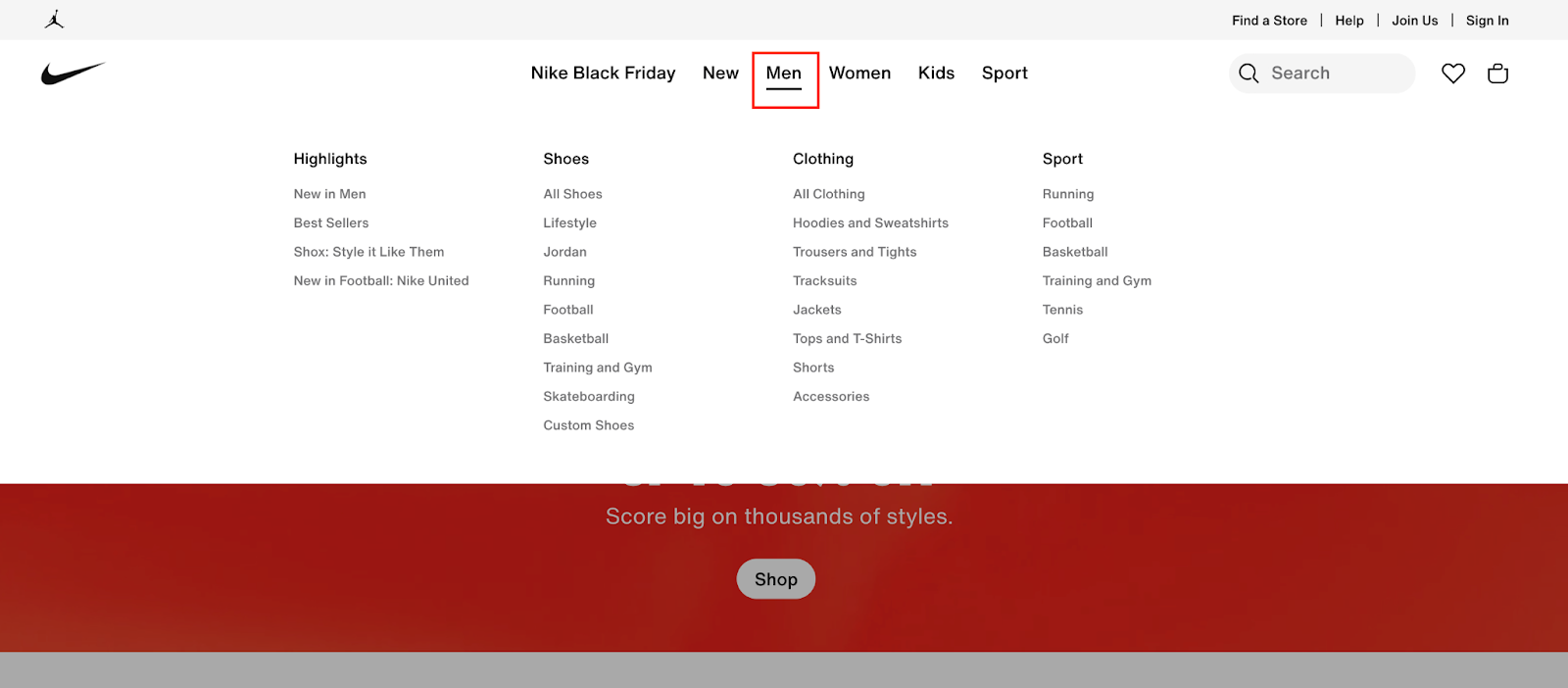
Build a flat, organized site structure with logical hierarchies
Your website should have core categories, then subcategories under each category. Insert a clear navigation menu reflecting your site’s hierarchy. The standard method is having each category on the main navigation menu, then dropdown menus to display subcategories without cluttering the main menu. Here’s an example of a website with this hierarchical structure:
Optimize URL structure (short, keyword-rich, hyphen-separated)
Your website’s URLs should be as short as possible, separated by hyphens and incorporating relevant keywords, fondly called Friendly URLs. Suppose you have a blog post about “The best SEO tools for 2025,” the ideal URL structure would be [YourDomain.com]/blog/the-best-SEO-tools-for-2025, not [YourDomain.com]/blog/ht67htyuio78yetru. The former is precise and relevant, while the latter isn’t.
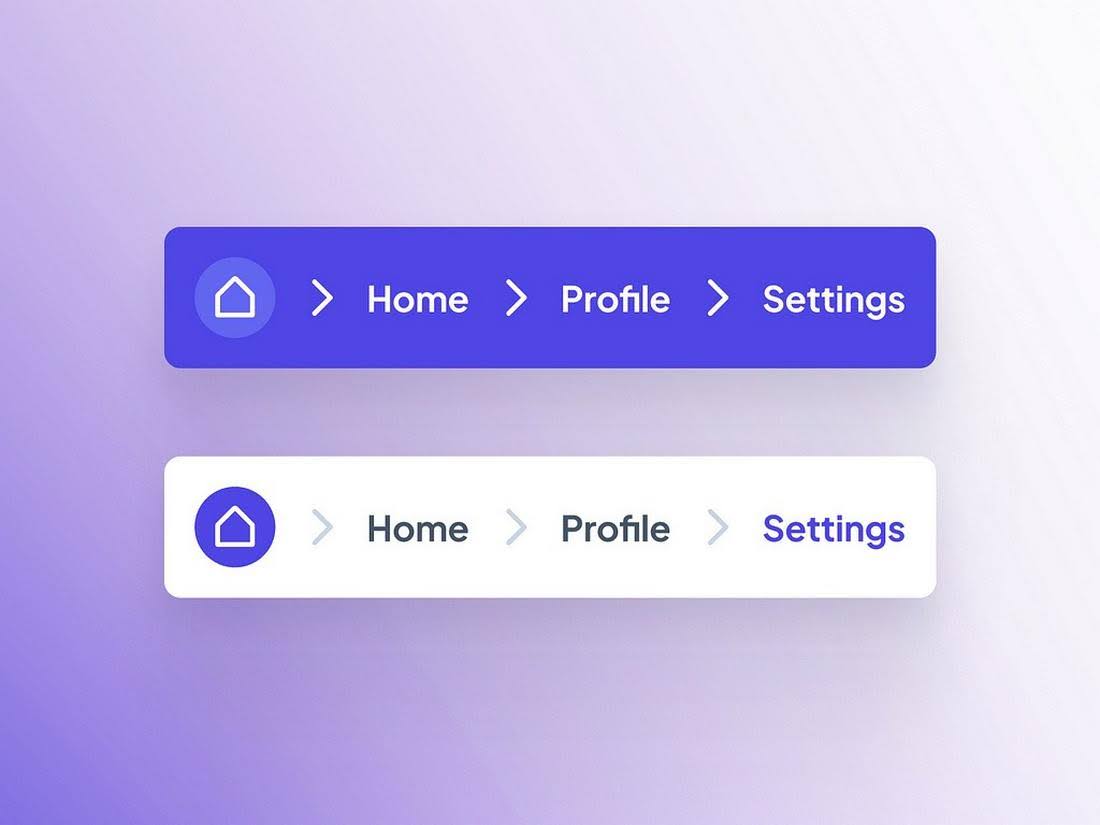
Use breadcrumb navigation to improve UX and SEO
A breadcrumb navigation system always indicates a user’s current location in your website’s hierarchy. For example, if someone visits your website, enters their profile, and then heads to settings, the navigation menu will display Home > Profile > Settings, with each heading being clickable.
With breadcrumb navigation, visitors can easily find their way back to a previous page. It prevents them from getting lost, so they stay longer on your site.
Identify and fix orphan pages (pages without internal links)
Orphan pages refer to pages without internal links. They aren’t ideal because internal linking helps search engine crawlers discover your content, leading to higher search rankings. With an SEO audit tool like Semrush, scan your website for orphan pages and add relevant internal links to them.
Improve internal linking strategy (contextual, descriptive anchor text)
It’s not enough to just have internal links. An effective internal linking strategy entails adding internal links with relevant text anchors. For example, when linking to a blog post about the best smartphones for 2025, a suitable anchor text would be best smartphones to use in 2025.
Mobile & user experience optimization
Over 60% of online traffic comes from mobile devices, illustrating how critical mobile optimization is for every website.
Mobile usability is a mandatory part of efficient technical SEO checklists — ignoring it means losing out on most traffic.
Let’s explore mobile optimization tips.
Ensure mobile-first, responsive design and site usability on all devices
Optimize your website’s visual elements to adapt to mobile displays. When adding new photos, videos, text, buttons, and other elements, consider small screens first before large PC screens. Test the site on a mobile device before deploying any changes.
Optimize site speed and performance (Core Web Vitals: LCP, INP, CLS)
Google uses three Core Web Vitals to evaluate web page performance: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) for loading performance, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) for responsiveness, and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) for visual stability.
Essentially, LCP measures the time taken for the largest image or text block to load on a page. INP evaluates the delay between a user’s interaction with a visual element and the response, and CLS measures how often users encounter unexpected visual element shifts. Pay attention to these factors and optimize your website accordingly.
Monitor and improve loading times (PageSpeed Insights & other tools)
Your web pages should load quickly, preferably under 2 seconds. Some effective page speed optimization tips are compressing images to minimal sizes, removing any unnecessary visual elements, and using a content delivery network (CDN) to load your content from servers closer to each visitor’s location.
Enhance overall UX signals (dwell time, CTR optimization, page engagement)
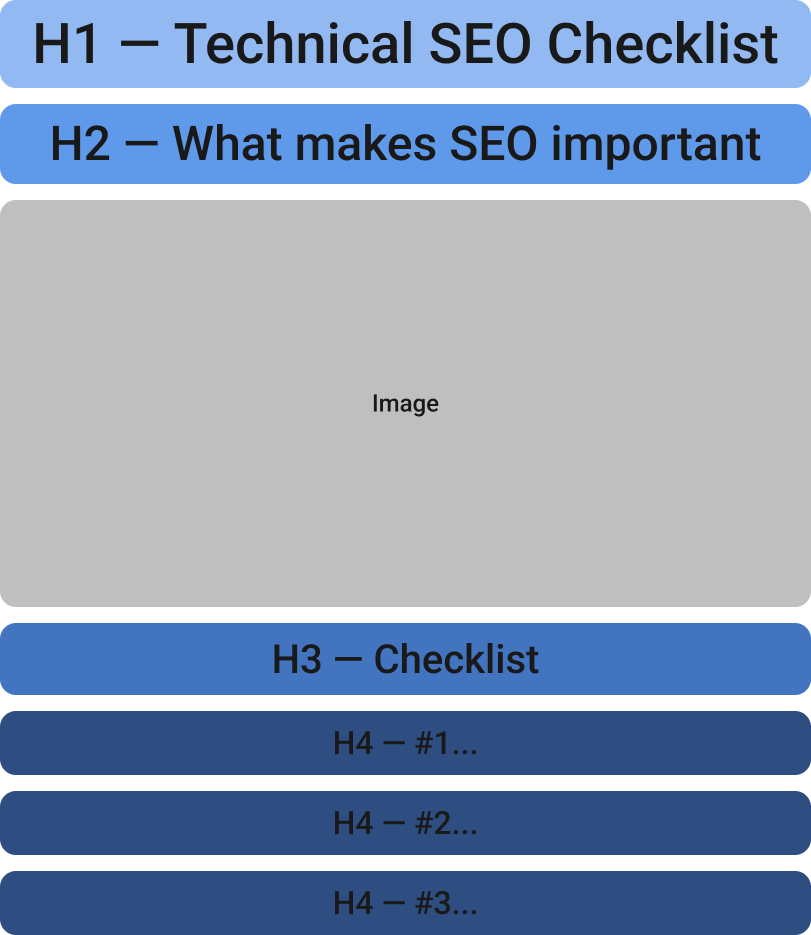
Pay attention to general user experience optimization to increase signals like dwell time (how long people stay on your page before going back to search results) and click-through rates. You can improve these metrics by integrating graphics into posts, streamlining navigation, and using clear formatting and headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to make content readable.
Below is an illustration of a clearly formatted web page that’s easy to read and enhances the user experience.
Implement the best security practices beyond HTTPS (hosting, data handling)
Even when your website is HTTPS-secure, don’t forget to use strong passwords, implement access control, and enable two-factor authentication on your CMS. Create regular site backups so that you can restore a previous version if a security incident occurs. Conduct regular security audits to identify and fix flaws that could be exploited.
Content & metadata technical health
Technical SEO checklists aren’t complete without discussing content and metadata health. Adding meta tags, fixing broken links, and implementing structured data markup are impactful SEO tasks. Let’s dive deeper into these tasks.
Identify and improve thin content pages
Scan your website for thin content pages with little word counts and minimal engagement. You can do this manually or use SEO tools to automate this process. With an SEO tool, like Semrush and Ahrefs, you’ll initiate a comprehensive site audit, and it’ll alert you about any identified thin content pages. After identifying a thin content page, you can add more relevant content, redirect it to another page, or delete it altogether.
Ensure each page has optimized metadata (title tags, meta descriptions)
Always place relevant keywords in your page titles and meta descriptions. These keywords tell search engines what your page is about, leading to increased visibility. Along with titles and descriptions, you should also insert relevant keywords in the URL, page body, and alternative text for images.
In the above table, the good title tags have relevant keywords and precise descriptions. They are neither too short, like the bad examples, nor too long to be indexed by search engines. They fit perfectly.
Optimize ALT text and file names for images
Every image should have a relevant name and an attached alternative text. For example, an image of a car can be named “[CarName].jpg” and the alternative text will be “A [CarName] parked on the road.” This relevant name and alt text let crawlers index the image accurately and suggest your site when someone searches for an image related to the car.
Implement structured data/schema markup
Schema markup refers to code added to your website to help search engines understand its context. For example, in an online store, Schema code points search engines to product listings with specific prices and star ratings. This way, the search engine indexes the product listing and displays the correct price to users. Implementing schema markup helps search engines create rich snippets for your site.
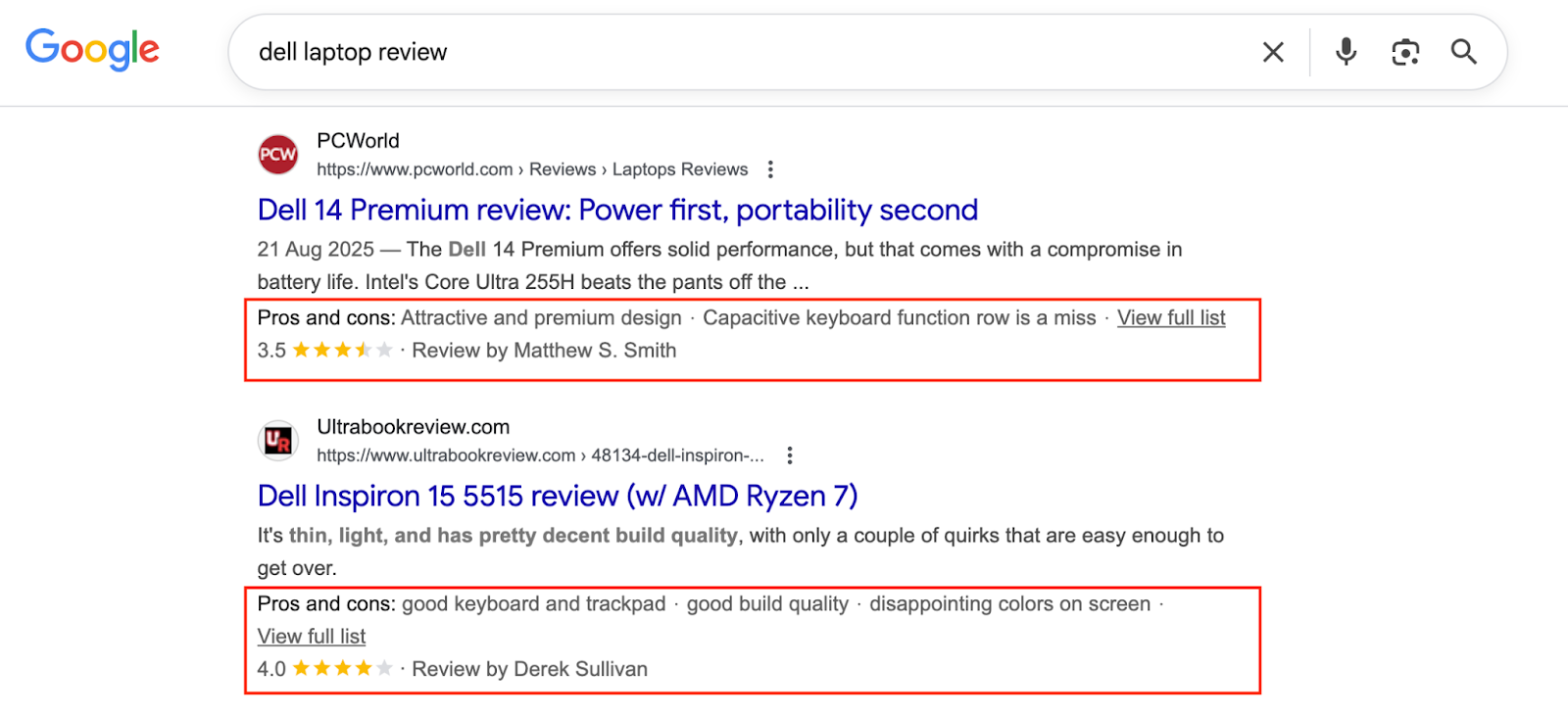
Audit and eliminate broken internal and external links regularly
Identify page links that no longer point to an existing page, then delete them to avoid directing users to error pages. Broken links emerge when an existing page is renamed, moved, or deleted without the URL being adjusted. You can use an SEO tool like Semrush to scan your site for broken links, then delete them in one swoop.
Fix server errors (5xx errors) promptly
Fix any server-side errors to avoid users running into error pages and having a bad experience. Common server errors are 502 Bad Gateway, 503 Service Unavailable, and 504 Gateway Timeout. You can fix these issues from your website’s content management system.
Advanced technical SEO
Technical SEO checklists also cover advanced factors like voice search optimization, lazy loading, and JavaScript rendering. Let’s explore these expert SEO techniques.
JavaScript SEO considerations (crawlability, rendering)
If your website has JavaScript-based content, prioritize server-side rendering over client-side rendering. Excessive client-side rendering affects page speed and, consequently, search rankings. Server-side rendering leads to faster page loading and search crawling.
Manage paginated content properly with rel=“next” and rel=“prev”
If a website section contains multiple pages, use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” to show search crawlers the relationship between these pages. Otherwise, all pages might be considered a single mass of content and indexed incorrectly.
Use lazy loading for images and assets without hurting Core Web Vitals
Lazy loading is a technique where images on a page aren’t loaded until a user scrolls to them. It reduces page load times, as all the images won’t have to load at the beginning. It also provides a better user experience by minimizing the strain on a user’s device.
To implement lazy loading, you’ll need to tweak your website’s backend code or install an external plugin on your CMS. Choose the plugin option if it’s available on your CMS, as it’s easier to set up.
Optimize for voice search and emerging search technologies
Voice search is an emerging search trend that shouldn’t be ignored. Optimize your site to benefit from this trend by providing precise answers to search queries, writing in a conversational tone, and providing location-specific information for readers.
Time to sort out your technical SEO
Audits, fixes, structure, performance — we take over the technical load at any stage of your site’s lifecycle.
Monitoring & continuous improvement
After implementing the SEO checklist, monitor for improved results and adjust your strategy as needed. This monitoring covers log file analysis, rich result testing, regular SEO audits, and staying up to date on search engine algorithm changes.
Use log file analysis to monitor bot activity and crawler behavior
Examine your server log files to identify the web crawlers visiting your website, which content they access, and how often they access this content. Log analysis shows which parts of your website are frequently crawled and whether there are obstacles to efficient crawling. You can analyze log files manually or use a designated analytics tool, e.g., Datadog.
Regular technical SEO audits using tools like Semrush, Screaming Frog
Frequently audit your websites using SEO tools like Semrush and Screaming Frog. These tools completely analyze your website to point out SEO flaws that need to be fixed, like broken links, thin content, orphan pages, and improper meta tags. A lack of frequent audits will let these issues fester and drag down search rankings.
Monitor Core Web Vitals and fix issues continuously
We discussed Google’s Core Web Vitals earlier: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and what each measures. Continuously monitor these vitals and follow Google’s recommendations to improve your site’s performance.
Use rich result testing tools to validate structured data
Use Google’s free Rich Results Test Tool to validate if your site has structured data that enables Google to show rich snippets. If not, you should implement structured data to improve search performance.
Stay updated on Google algorithm changes and evolving SEO best practices
Google regularly adjusts its search algorithms and discloses the adjustments. To stay updated on algorithm changes, visit Google’s Search and SEO blog and subscribe to the RSS feed. Also, subscribe to the Google Search Central YouTube channel for live illustrations of the algorithm changes.
Bonus: Link building & digital PR for technical SEO
Link building means getting backlinks from other sites. These backlinks are like a vote of confidence from search engines, confirming that your site is good enough for other sites to direct readers to. The more backlinks acquired from relevant sites, the higher your search rankings and industry reputation.
Strategies for earning high-quality backlinks
To get backlinks, create quality content with rich information, publish guest posts on other sites, fix broken links, and provide a good user experience. These factors encourage other site owners to link to your content willingly.
Fixing technical issues that impact link equity flow (redirects, canonicalization)
Fix crawl errors and other issues concerning canonical tags implementation, robots.txt optimization, XML sitemap submission, and meta tags optimization. These technical fixes ensure your site remains discoverable to generate backlinks.
Leveraging content assets for journalist coverage and backlinks
Publish high-quality visuals, research and data reports, industry case studies, and interviews with industry experts. These constitute valuable content that’ll encourage journalists to link to your content.
Conclusion
This checklist covers the key technical SEO tasks to stay competitive in your niche. From crawling to site architecture, mobile experience, metadata, advanced SEO techniques, and continuous monitoring, we’ve got you covered.
FAQs