Contents
Content no longer needs only a high position in search results. It also needs to show up in answers from ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and other AI agents. For businesses, that means brand visibility in search is not the same as visibility online.
This is where GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation) comes in. It builds on classic SEO but is designed for language models. The point is to help your content get cited in AI answers.
This article was prepared by Ivan Sivakov, Senior SEO at Why SEO Serious. Ivan has worked in SEO for almost ten years. He has led projects for online stores and broader e-commerce, as well as medical and education portals. He has seen how search systems evolve and what drives growth in competitive niches.
In this guide, he explains how answers in ChatGPT and other AI agents are built and how GEO helps content earn a place in those answers.
What GEO, AEO, and AIO mean
To understand how content gets into AI answers, it helps to separate three related directions: GEO, AEO, and AIO. All are connected to AI, but they solve different tasks.
GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) is adapting content for LLM answers: ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, or Gemini.
An LLM does not read a page end to end. It looks for fragments that fully answer the query and can be reused in a generated response without edits. GEO focuses on making content structured, reliable, and easy for language models to interpret, so those fragments are the ones selected.
AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) is optimisation for AI answers inside search experiences, such as Google AI Overviews and similar AI-generated result blocks.
This includes work on featured snippets, knowledge panels, and carousels. The goal is close to GEO: structure information so an AI system can use it as a ready answer to a user’s query.
AIO (Artificial Intelligence Optimization) combines GEO and AEO and covers site optimisation as a whole: technical health, reputation, and link profile. Beyond text, LLMs also evaluate whether a site is authoritative, whether it is cited by other sources, and whether content is kept up to date. These signals influence whether the system should use the site at all.

Why show up in AI blocks and chatbots
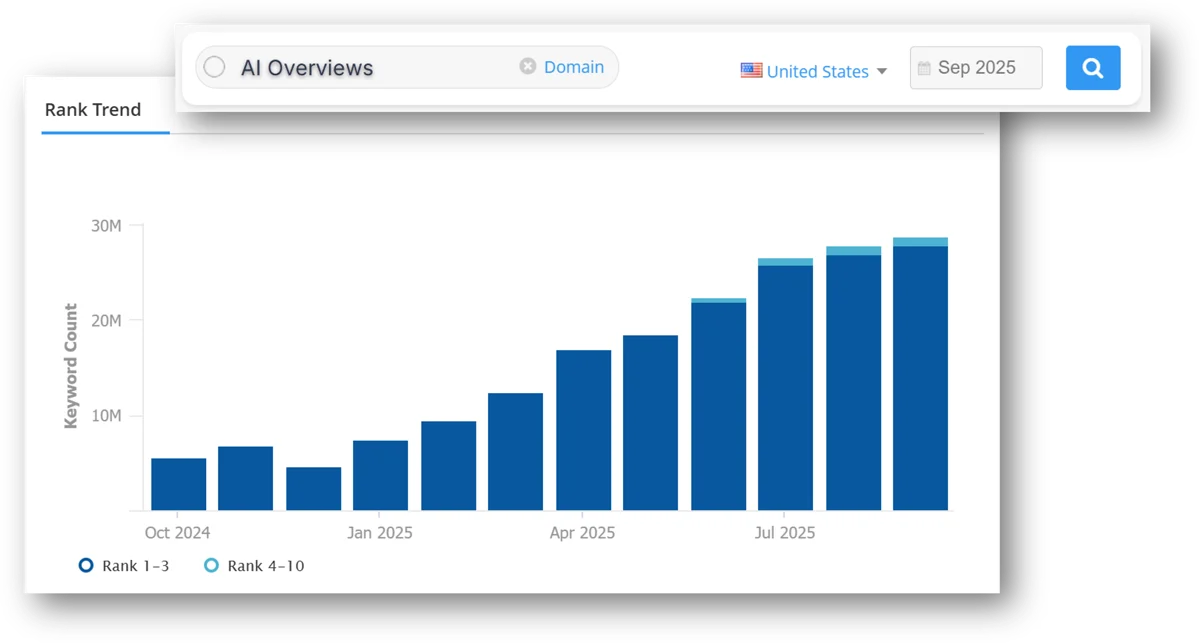
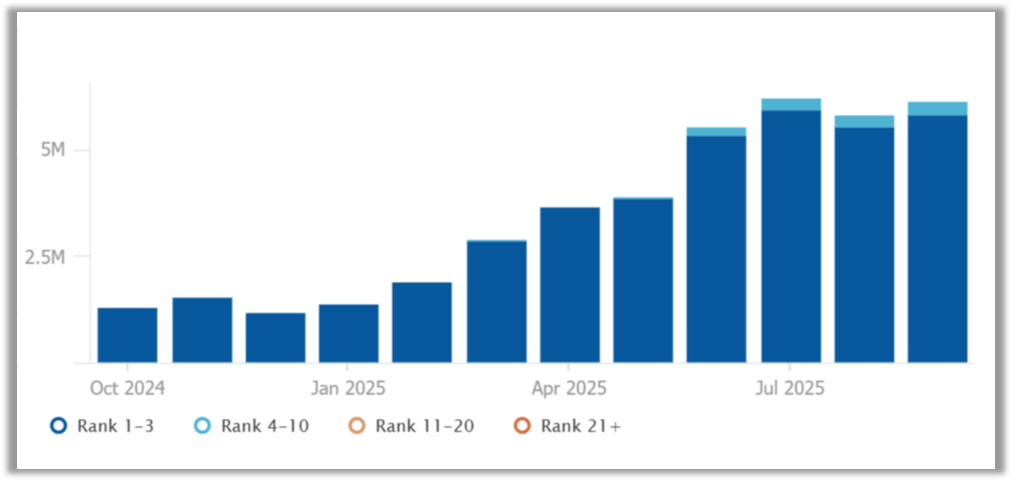
AI Overviews are becoming a standard part of Google results. Search Engine Land reports that the share of AI Overviews in Google grew from 10% in March 2025 to 30% in September, a new high.
On mobile, the change was even sharper. The appearance rate of AI blocks increased 474.9% year over year. In over 90% of AI Overviews, the sources come from the top 10 organic results.
These blocks affect more than informational queries. They also shape behaviour in buying journeys. According to SEOClarity, from September 2024 to September 2025, the number of AI Overviews in transactional queries grew by about 492.2%, and AIO presence in the UK increased by 536.6%.
At the same time, the logic behind answer generation is changing. Google is pulling generative results closer to classic search. If earlier Google’s AI agents could produce overviews independently from organic rankings, the gap is now minimal. A Search Engine Land study (September 2025) found that 99.5% of AI answers overlap with content from the top 10 organic results. Earlier in the year, the gap was 93.8%.
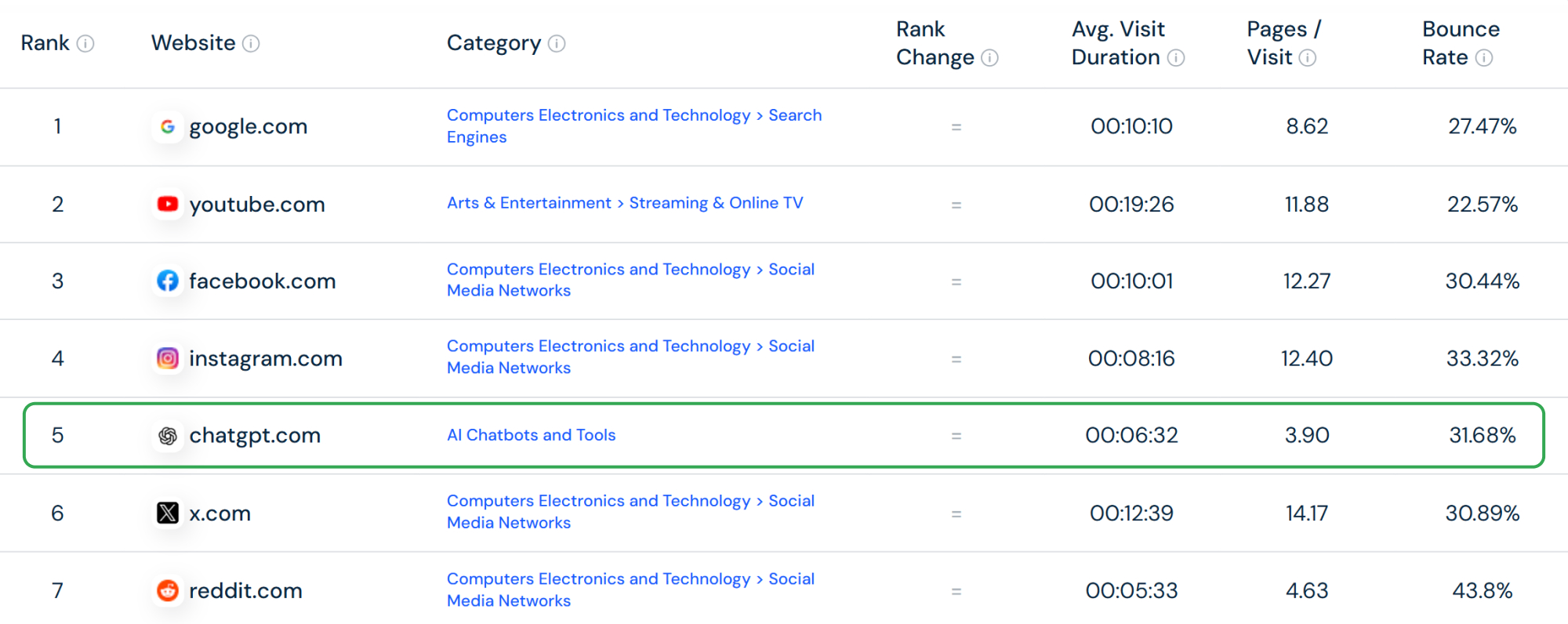
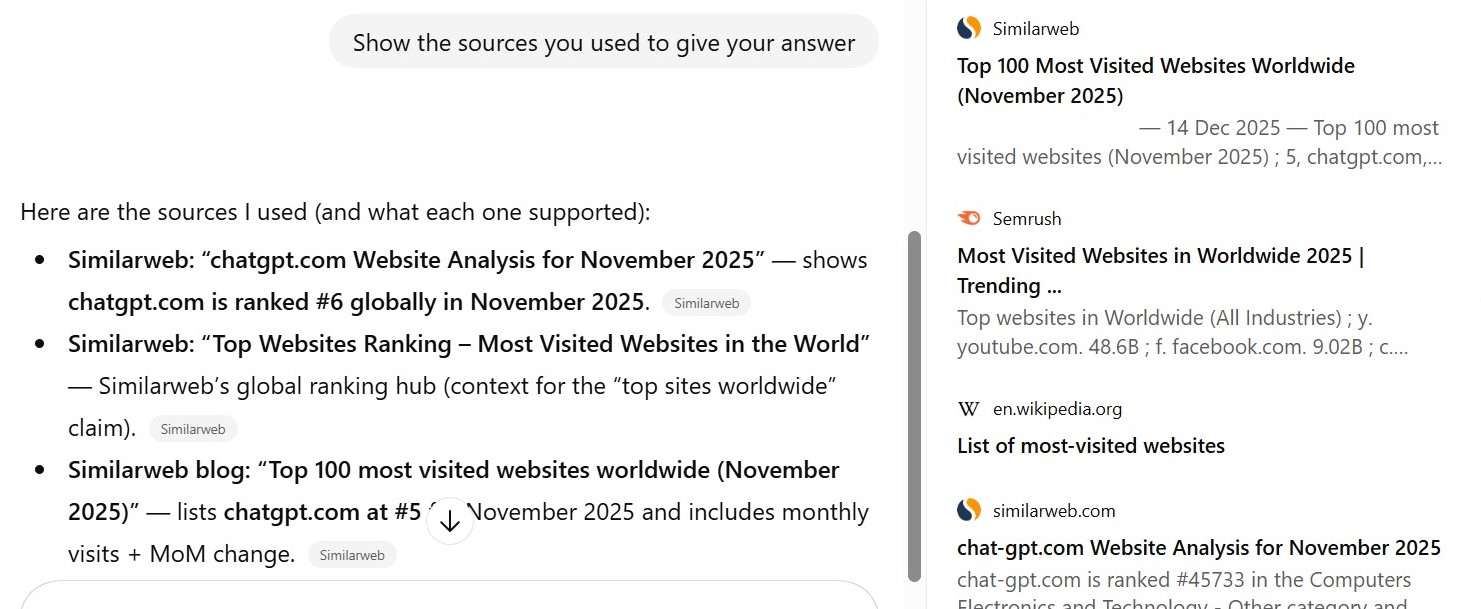
The impact of generative systems goes beyond search. Similarweb places ChatGPT in the top 5 most-visited websites worldwide. AppFigures also shows that the app consistently stays among the most downloaded in the world.
AppFigures also shows that the app consistently stays among the most downloaded in the world.
A new behaviour pattern is forming. A user refines a question in an AI interface, gets a short overview, and then goes to classic search to narrow down options.
For brands, this shifts the meaning of visibility. AI answers add an extra layer: a chance to be noticed before a click.
The scale of change is comparable to earlier turning points, such as the rise of search engines in the 1990s and the mobile shift of the 2010s.
We are entering a period where AI becomes the main interface for search. How quickly brands adapt to this model will shape their position in the future digital landscape.
How to optimise a site for GEO and LLMs
Most optimisation principles still apply. What changes is the target. Rankings still matter, but it also matters whether an AI system understands the content and trusts it.
1. Strengthen E-E-A-T: expertise, experience, authoritativeness, trust
LLMs evaluate sources using a set of signals similar to classic E-E-A-T. The goal is to show that content is created by professionals and built on verifiable data.
- Add the author and their credentials.
- Add publication and update dates.
- Support claims with research, quotes, and statistics.
- Link to primary sources and reputable publications.
- Show first-hand experience, for example: “based on audits of 100 projects” or “based on our internal study”.
2. Structure content
LLMs analyse structure, relationships, and context. The clearer the organisation, the higher the chances that the system will extract relevant facts.
- Use a clear heading hierarchy (H1–H6).
- Add Schema.org structured data:
FAQPagefor Q&A blocks.HowTofor step-by-step instructions.Articlewith author and date.Product, Reviewfor product pages and reviews.
- Add tables, lists, and quotes. They make machine extraction easier.
3. Answer directly and precisely
Generative systems value precision. If a page includes clear answers to common questions, the chance of being used in an AI overview increases.
- State questions explicitly: “What is GEO?” “How do LLMs work?”
- Right after the question, give a short, factual answer.
- Then expand the topic in detail. This format works well for both readers and models.
- Use a Q&A block with
FAQPagemarkup at the end of the article.
4. Work with long-tail queries
Conversational, specific long-tail queries are a major source of natural traffic for generative systems. People ask the way they speak, for example, “How to choose a monitor for design” or “Where to eat nearby.”
- Analyse autosuggestions and related search phrases.
- Use natural language and varied phrasing (LSI terms).
- Add content built around real user scenarios.
5. Use facts and details
- Use lists, tables, and side-by-side comparisons.
- Avoid vague statements. Instead of “many users say,” use something like “in our survey, 68% of users…”.
- Update content. Outdated information loses authority for LLMs.
- Review tables, numbers, screenshots, and links regularly.
Note: changing only the publication date will not work. Search engines and LLMs compare the on-page content with cached versions. Updating dates without real edits can hurt both SEO and GEO.
6. Account for the new user journey
In many cases, an AI answer fully covers a simple query, and the user does not click through.
That makes the page a “next step” after the AI answer. Content needs enough depth that both the reader and the model still want to go further. For example: “To understand the nuances, explore the step-by-step guide and case studies on our page.”
What matters most is added value. A solid article is not enough on its own. Content needs elements that an AI system cannot generate without original inputs:
- First-party reports and research.
- Original methods and detailed how-to materials.
- Interactive calculators, checklists, and real examples from practice.
This is what signals unique data and experience, rather than a rewrite of what many competitors already publish.
7. Improve visibility in Google and Bing
ChatGPT and some other LLMs partially build answers using the indexes of Google and Bing. Google is usually in place. Bing often isn’t. Submitting the site and monitoring it in Bing Webmaster Tools is a required step for a GEO strategy.
- Check the indexing status of key pages.
- Monitor technical issues.
- Compare rankings in Bing and Google. Differences can point to Bing-specific priorities that matter for AI answers.
OpenAI does not disclose the exact search system it uses. In AI solutions for large organisations and education projects, they have confirmed Bing usage.
When GEO needs a hand
Our team helps companies earn citations in ChatGPT and other AI products, including Google AI Overviews and Perplexity. We turn GEO into a clear set of technical and content tasks, then help implement them.
Checklist: How to optimise a site for GEO and LLMs
| What to do | How it works |
|---|---|
| Strengthen E-E-A-T |
Show expertise and experience. Add authors, cite sources, and include research-backed data.
Evidence builds trust for both search and LLMs.
👉 More on building E-E-A-T: read the full guide . |
| Structure content | Use H1–H6, tables, and lists. Add Schema.org markup (FAQPage, HowTo, Article) to help systems extract meaning and relationships. |
| Focus on long-tail queries | Target conversational and voice-style phrasing. Use natural language and LSI terms. |
| Update data | Check that numbers and links are current. Do not change publication dates without real edits. |
| Optimise for real users | Cover the topic in depth. Avoid keyword repetition. Add unique content and first-party data. |
| Account for the new journey | AI answers reduce clicks. Make content worth continuing with: case studies, reports, calculators, and methods. |
| Monitor Google and Bing | Check indexing, fix errors, and track rankings. This increases the chance of being used as a source in AI answers. |